Spot Trading: A Comprehensive Guide to Cryptocurrency Spot Transactions

Understanding Spot Transactions in the Cryptocurrency Domain
When delving into the realm of virtual/cryptocurrency, terminologies such as “spot,” “spot market,” and “spot trading” might be perplexing. Spot trading involves the immediate execution of transactions with immediate delivery of assets and payment.
What is Spot?
Spot trading refers to the immediate purchase or sale of a commodity, financial instrument, or cryptocurrency that is settled (delivered and paid for) on the spot date, which is typically the normal settlement day for the particular asset being traded. The term has roots in traditional markets where it originally meant trading tangible assets like gold or commodities directly and physically. However, with the advent of electronic trading, “spot” has come to mean any immediate exchange, including financial securities like stocks and even digital currencies.
For instance, in the realm of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), or Tether (USDT), engaging in a spot market means that you buy the digital currency and it is immediately transferred into your digital wallet. From there, you hold the actual coins and can freely transfer them, use them for transactions, or participate in crypto-related activities such as staking or governance.
In contrast, a futures contract, which is the opposite of a spot trade, involves an agreement to buy or sell an asset at a future date at a predetermined price. While spot trades involve immediate settlement, futures contracts are about speculative trading on the future price movement of an asset.
To put it in more practical terms, if you’re buying a stock or cryptocurrency on the spot market, you’re paying the current market price and taking possession of that asset right away. If you’re dealing in futures, you’re agreeing on a price now, but the transaction will happen later. This distinction is crucial for investors and traders to understand when navigating both traditional and crypto markets.
Spot Markets: Trading Assets on the Fly
Spot markets are where you can trade assets immediately. These markets allow people to buy and sell things like stocks, gold, and currencies right away, without having to wait. From physical goods to financial products, the spot market has it all.
Here’s how it works: when you trade on the spot market, you and the other person in the trade have to settle the deal right then and there. For stocks, places like the NASDAQ are where these instant trades happen. Gold and currencies have their own markets too.
For trading cryptocurrencies, you can use exchanges like 8V, which are open 24/7. You get live updates on prices and can trade cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum whenever you want. And with crypto, there are two kinds: those you can trade on centralized exchanges and those on decentralized ones, each working a bit differently.
Centralized Exchanges (CEX):
Listed according to CoinMarketCap’s exchange rankings:
- Binance
- Coinbase Exchange
- Kraken
- Bybit
- KuCoin
For the complete ranking, you can visit CoinMarketCap’s official website: CMC Official Website
8V exchange integrates WEB 2.0 and WEB 3.0 for digital asset trading, offering over 200 spot trading pairs. Here, you can find a variety of coins to analyze, invest in, and trade cryptocurrencies. Its intuitive interface is user-friendly, making it a good place to build your investment portfolio.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX):
- Uniswap
- dYdX
- Curve
- PancakeSwap
- Shushiswap
Spot Trading: A Fast and Transparent Transaction Method
Spot trading is the process of buying and selling assets in real-time on the spot market. Participants can engage in spot trading via stock exchanges or other trading platforms, ensuring quick and transparent transactions.
In essence, spot trading is like an immediate exchange—money for goods. After a purchase on the spot market, buyers typically acquire the assets quickly, akin to buying a drink at a local store.
However, the settlement process can vary by market. For example, the stock market often operates on a T+2 settlement system, meaning it takes at least two days after a transaction for the buyer to receive the stock.
Cryptocurrency spot trading, on the other hand, is less cumbersome. You can go to either centralized or decentralized exchanges and use their order books, swaps, or Automated Market Maker (AMM) platforms to trade. After the transaction, you quickly receive the cryptocurrency.
For instance, you could use 8V Exchange to swap BTC in your wallet for ETH, or buy BTC with USDT, and even utilize credit card purchasing options to trade cryptocurrencies with fiat money like USD or TWD.
Additionally, some people with specific needs might opt for P2P or OTC (Over-The-Counter) trading to transact in spot markets. These methods may take longer to achieve the desired price.
The primary ways to conduct spot trading in cryptocurrencies/virtual currencies are as follows:
- Orderbook Mode (Orderbook)
- Swap/Flash Trade (Swap)
- Automated Market Maker (AMM)
- P2P/C2C Trading (Peer to Peer)
- Over-The-Counter Trading (OTC)
How to Conduct Spot or Coin-to-Coin Trading on 8V Exchange?
Here are the steps to execute spot or coin-to-coin trades on the exchange:
Step 1: Access the Exchange Homepage
Firstly, navigate to the homepage of 8V Exchange.
Step 2: Enter the Spot Trading Page
On the exchange’s homepage, locate and click on the “Trade” option found towards the bottom of the page.
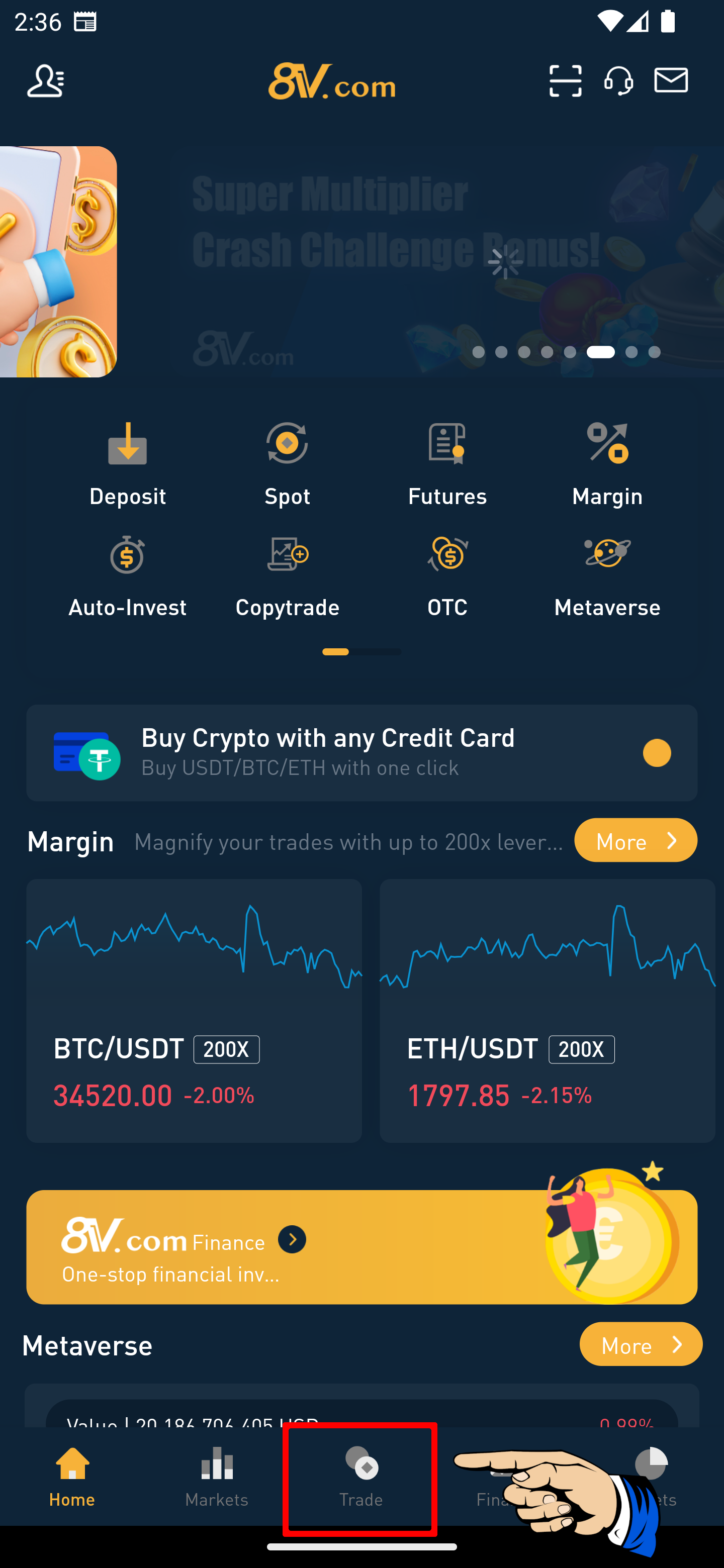
Step 3: Select a Trading Pair
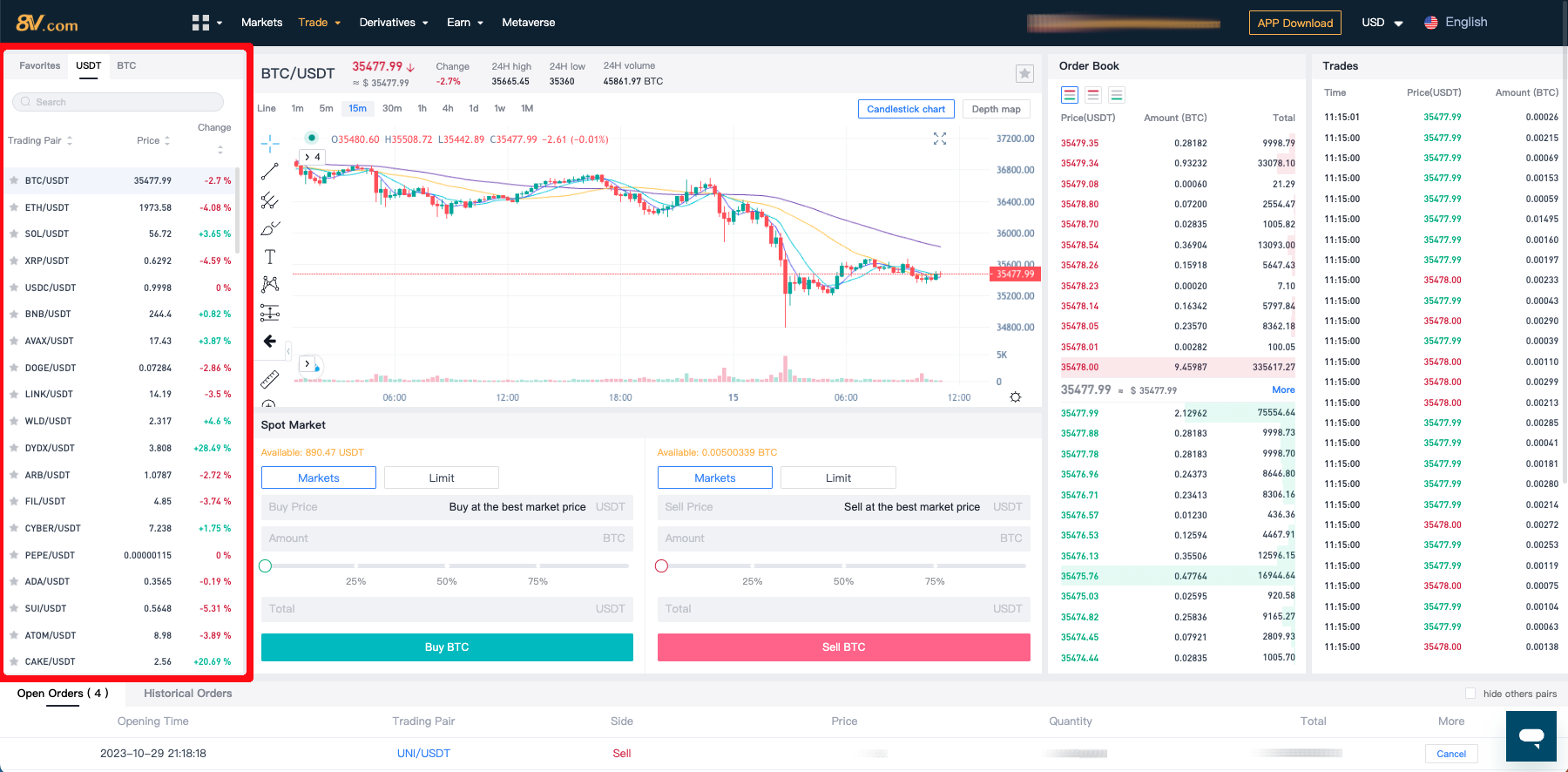
Once on the spot trading page, you can select the trading pair that interests you. For example, you might choose BTC to USDT or another cryptocurrency pair.
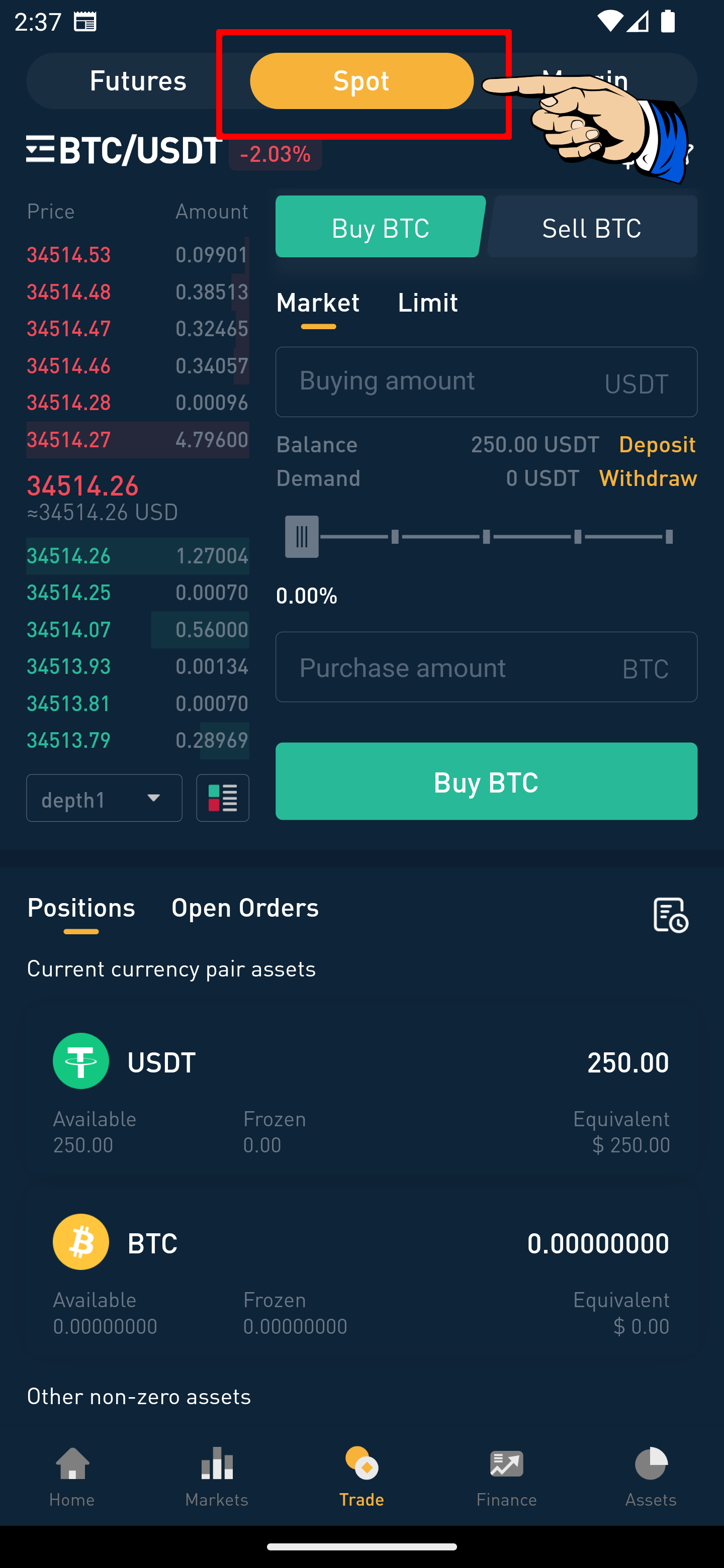
Step 4: Choose the Type of Order
Decide on the type of order you want to place, such as a market order or a limit order, along with any other relevant settings.
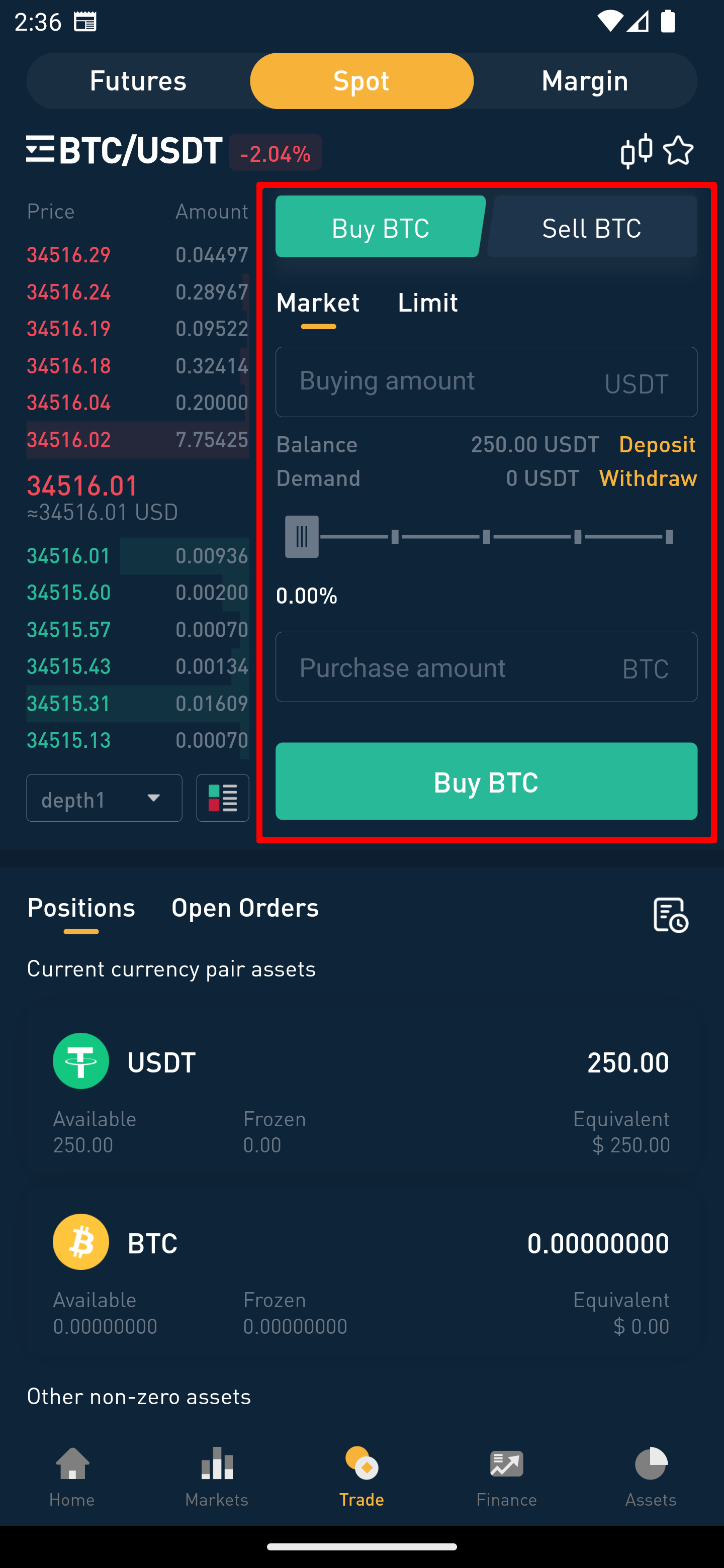
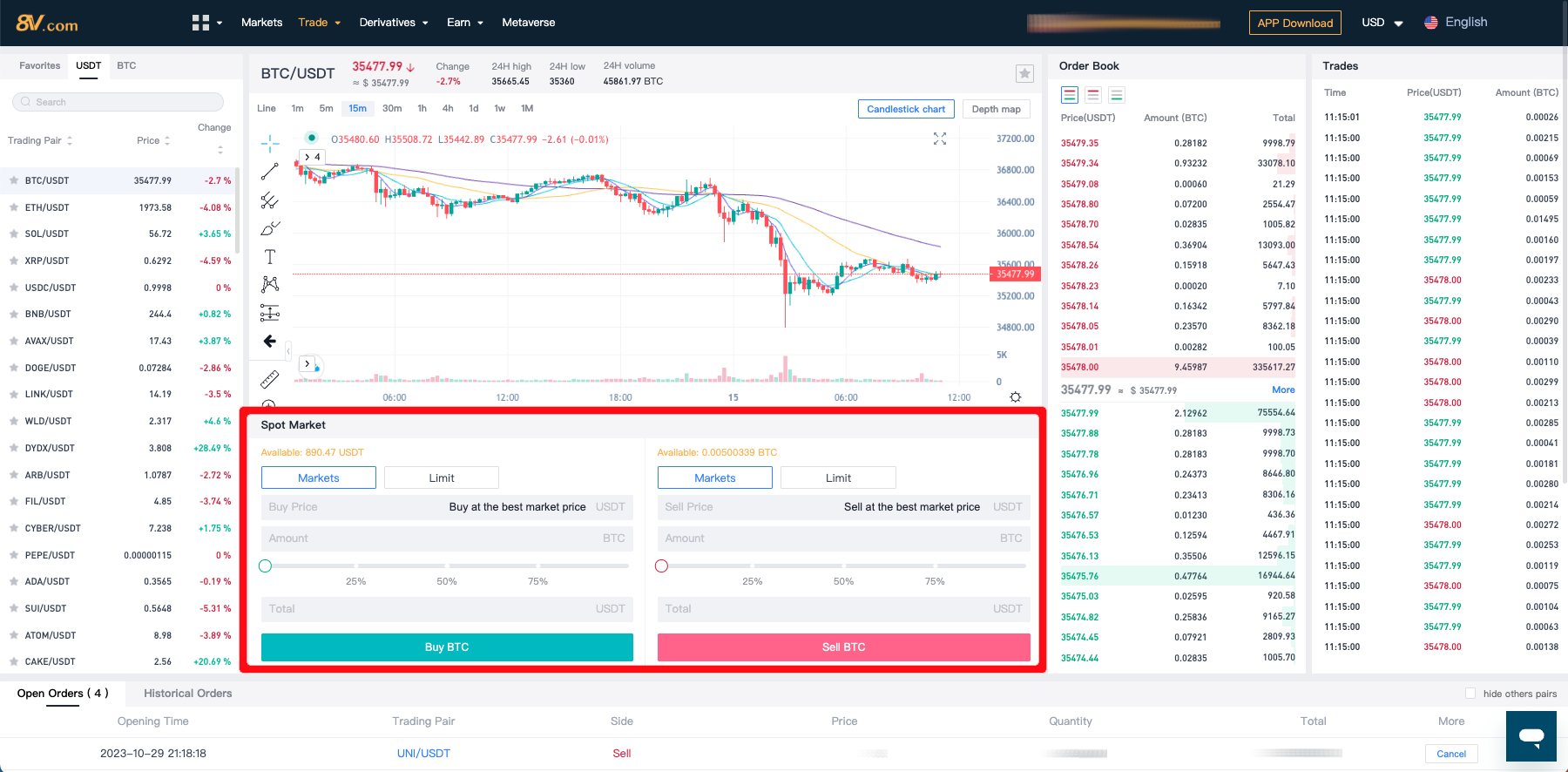
Step 5: Set the Order Details and Submit the Order
Enter the amount and price at which you wish to trade, then click “Submit Order”. Here, you can also choose between making an order or taking an order.
Making an Order (Maker):
This means your limit order is not immediately matched with an existing order and is placed on the order book, waiting for someone else to match it, thus adding liquidity to the market.
Taking an Order (Taker):
This refers to when your limit order or market order is immediately matched with an existing order on the order book.
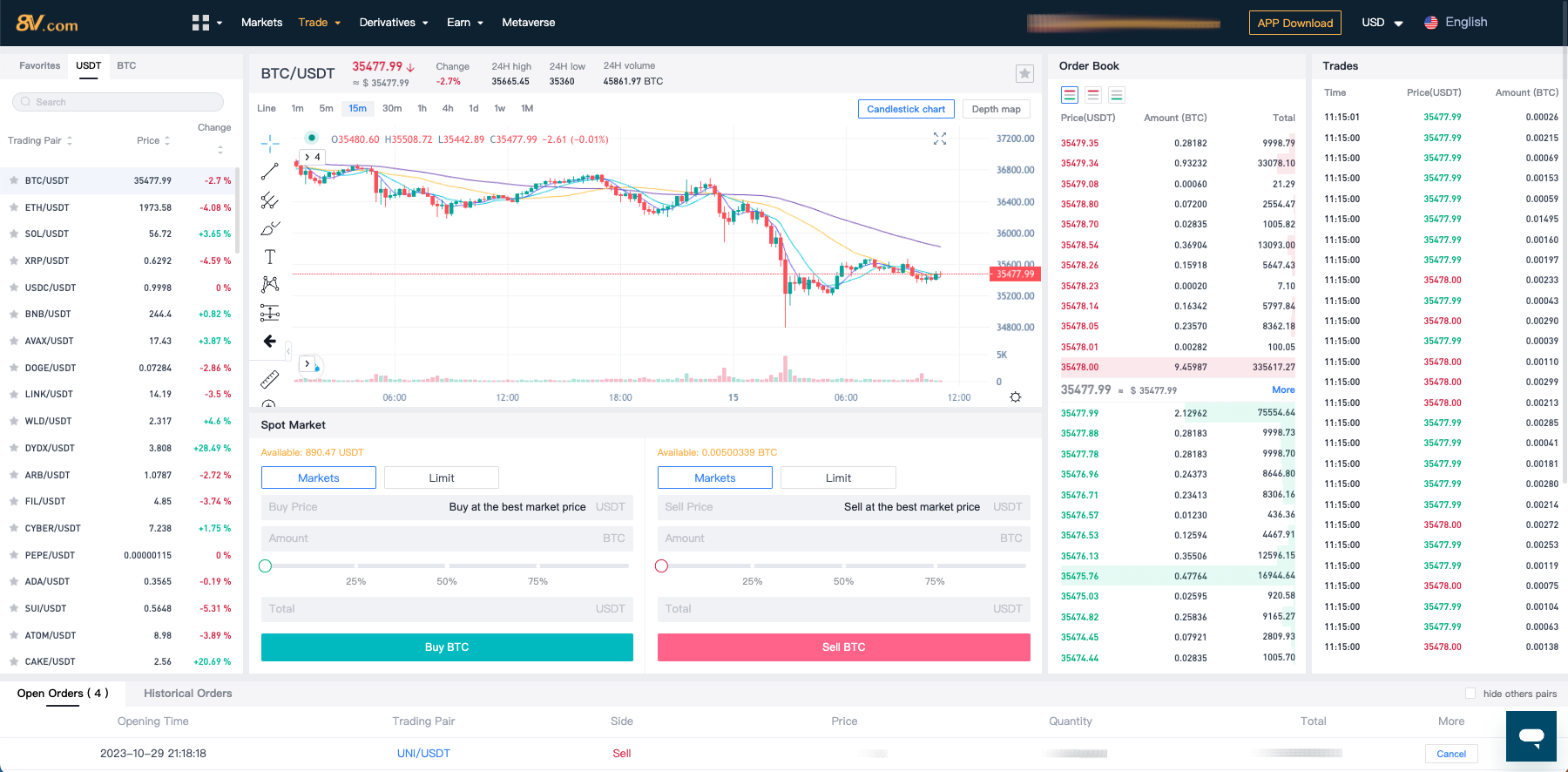
Spot Trading Page Explanation:
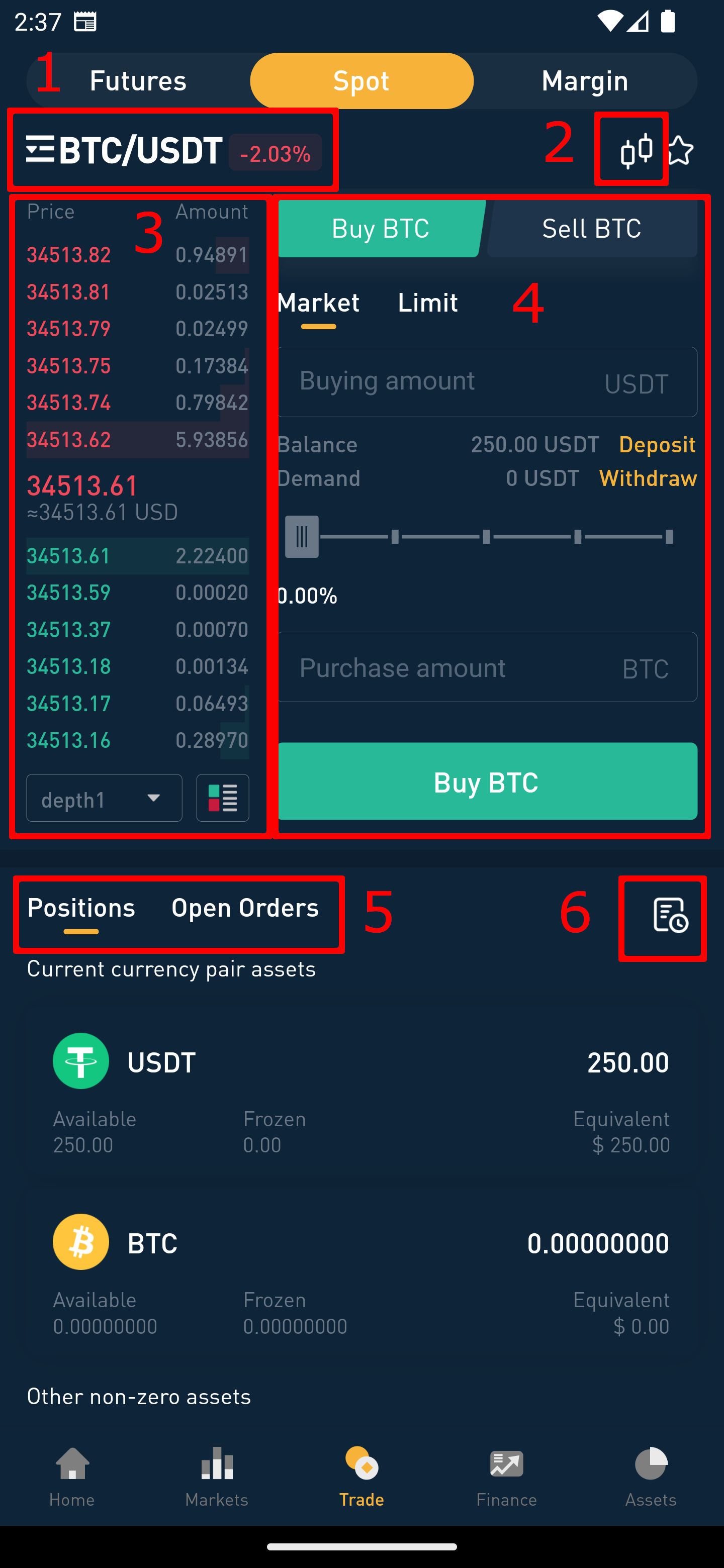
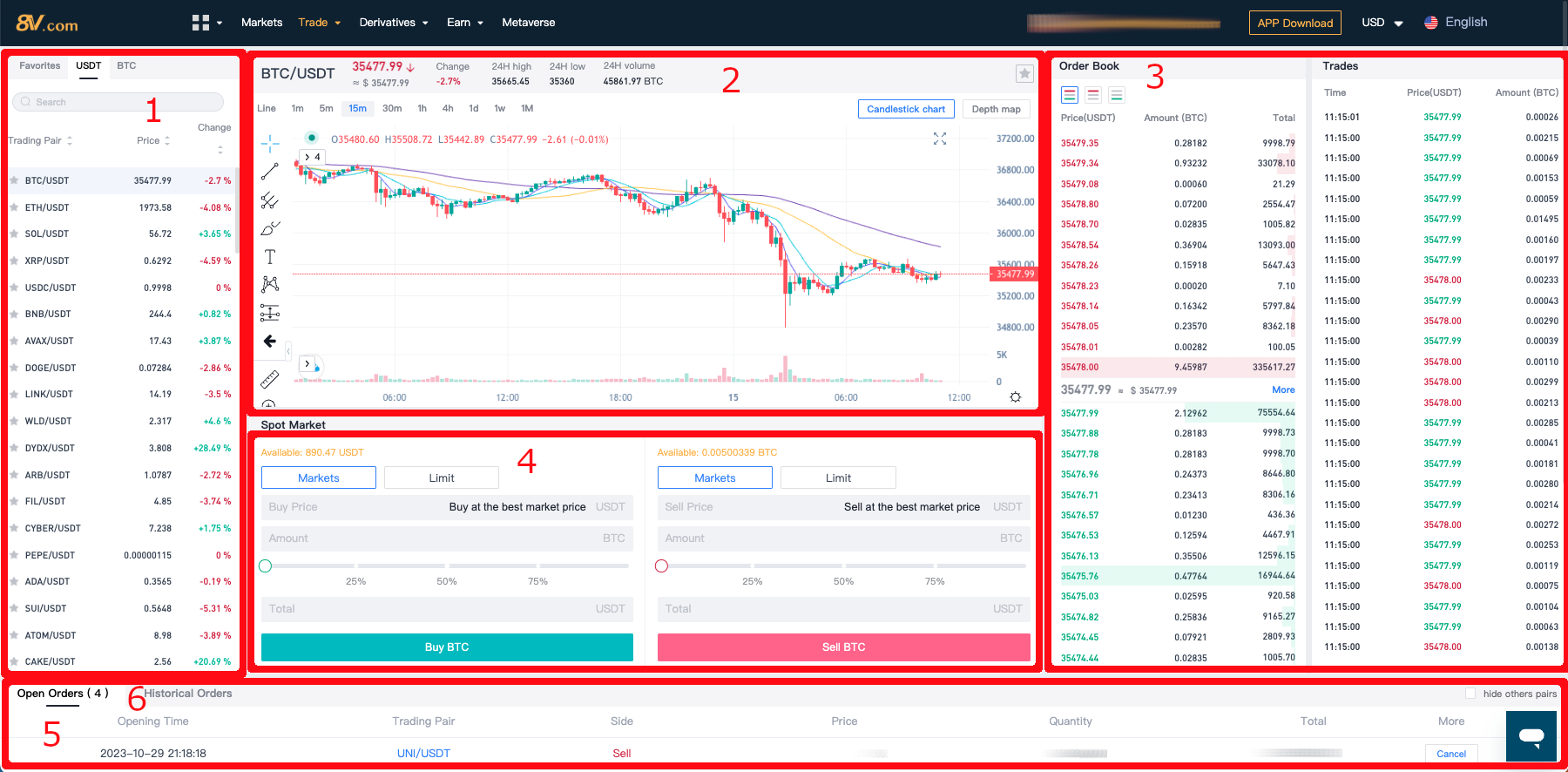
- Trading Pair Display/Switching Area: View and switch between the different trading pairs available.
- Real-Time K-Line Chart: Access the live K-line chart for price movements and trends.
- Open Buy and Sell Orders: Find all the current, yet-to-be-filled buy and sell orders here.
- Buy and Sell Order Zones: This is where you can create new spot transaction orders for buying or selling. In the trading center’s order placement area, refer to the prices in the buy and sell zones on the left, enter the desired purchase price and the amount/quantity you wish to buy, and click “Confirm Buy” to execute the trade. The process for sell orders follows a similar pattern.
- Current Open Order Record: Check your open orders that are active and pending execution.
- Historical Order Record: Review your past orders, including those completed and those that were canceled or expired.
Spot Trading Fees
| User Type | Direction | Maker Fee | Taker Fee |
|---|---|---|---|
| All Users | Buy | 0.09% | 0.09% |
| All Users | Sell | 0.09% | 0.09% |
For more trading fees and rules, please refer to this article: Trading Fees and Limits
Spot trading is a crucial aspect of the financial markets, offering investors opportunities to buy and sell a variety of assets. Through exchanges, participants can easily engage in spot trading and capitalize on market fluctuations for potential gains. Remember to thoroughly understand the market and its risks before trading to make informed investment decisions.
![[Action required] Your RSS.app Trial has Expired.](https://8v.com/info/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/rss-app-cfAqZL-75x75.png)








